DNS vs hosting: What's the difference between them?
Originally published: 28 December 2023
Commonly mistaken to be the same thing, but totally different

Understanding the Difference Between DNS and Web Hosting
Domain Name System (DNS) and web hosting are two fundamental concepts for running a website, but they serve different purposes. While both are essential, confusing DNS and hosting can lead to issues and headaches down the road. In this post, we’ll break down the key differences and help make sense of how DNS and hosting work together to get your site online.
DNS Explained
DNS stands for “Domain Name System” and it acts like the phonebook of the internet. Its job is to translate domain names that humans can understand, like example.com, into IP addresses that computers can use to route traffic, like 93.184.216.34.
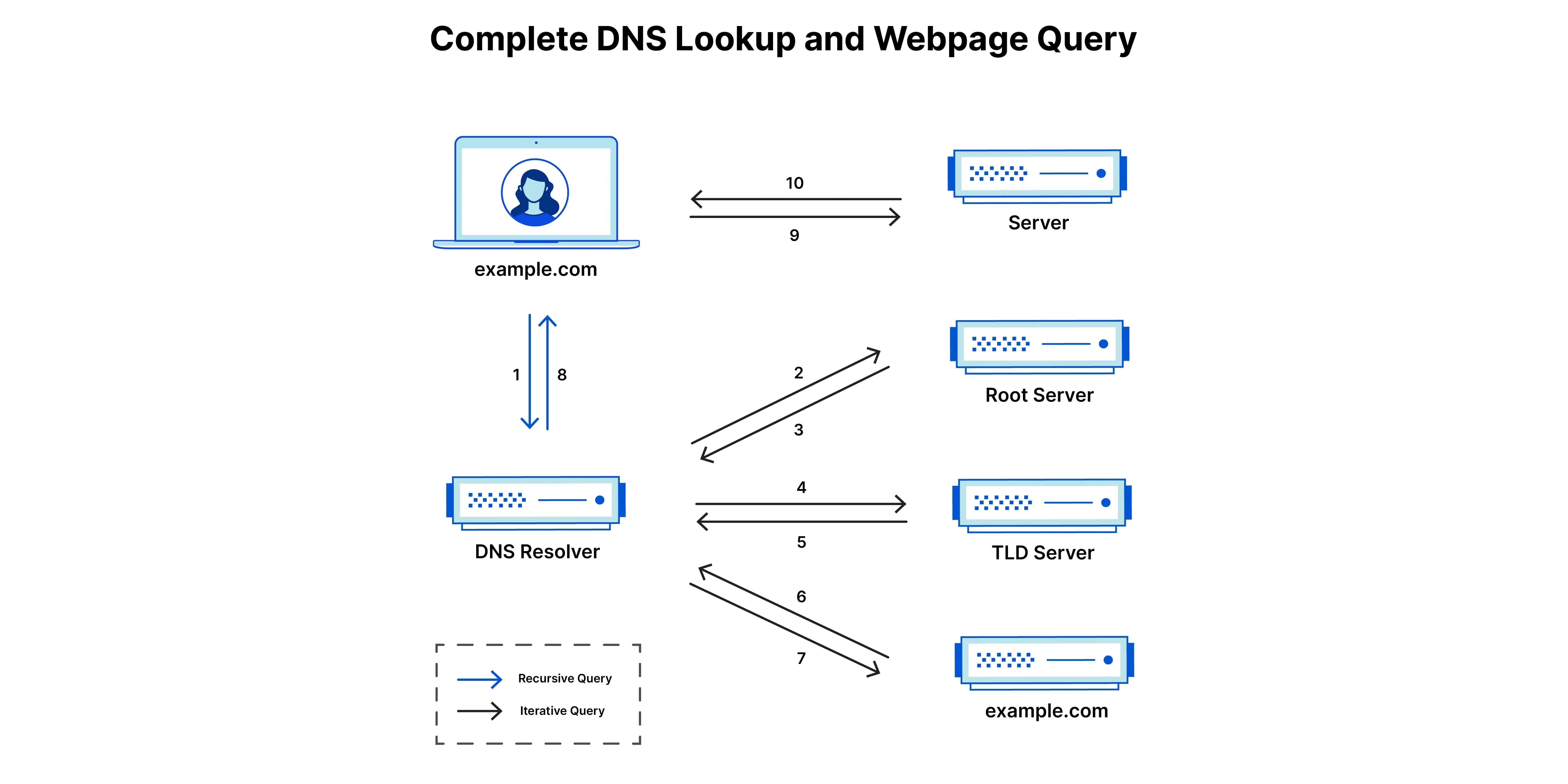
DNS servers hold these lookup tables that match domain names to IPs. When you type a domain name into your browser, a DNS query gets sent out to find the corresponding IP, so your computer can connect to the right server hosting that domain.
Without DNS, you’d have to remember all website IPs and manually enter them like http://93.184.216.34!
Some key things to know about DNS:
- Allows human-readable domain names to be translated into numeric IPs
- Is distributed across DNS servers around the world
- Requires registering and configuring your domain with a registrar
- Points your domain to the hosting server’s IP address
Web Hosting Explained
If DNS is like the address book, web hosting is like the actual house where your website lives.
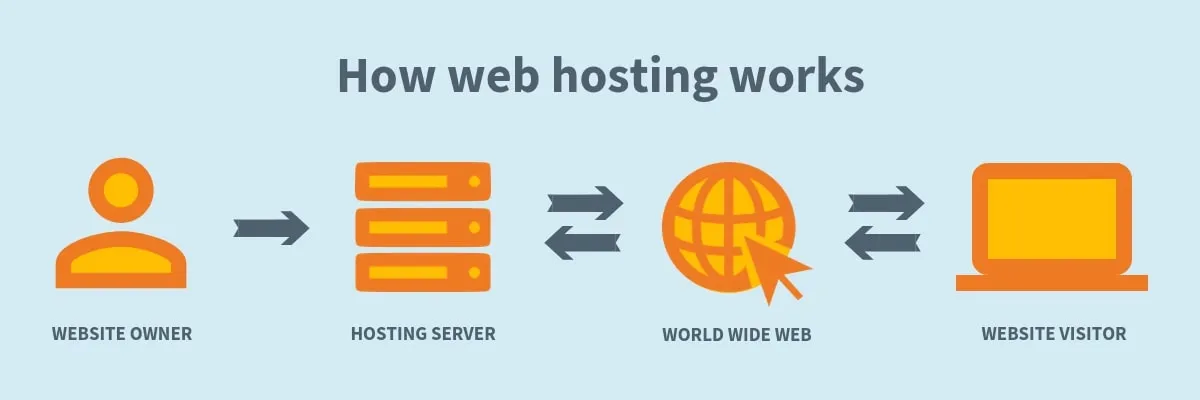
A web host provides the physical servers and technology needed to store your site’s files and deliver them from the server’s IP address. All the HTML, CSS, images, and other content for your site lives on these servers ready to be served to visitors.
Some key aspects of web hosting:
- Provides the actual servers your site is hosted on
- Enables your content to be accessed 24/7 online
- Offers options like shared, VPS, dedicated, and cloud hosting
- Requires a DNS record pointing your domain to the host IP
Without web hosting, your site would have no home on the internet. The DNS may point to the right address, but there would be no server there to answer the request.
How DNS and Hosting Work Together
When a user types your custom domain name into their browser, it triggers the following steps:
- Browser initiates a DNS query for your domain’s IP address
- DNS servers return the IP of your hosting provider
- Browser makes an HTTP request to that IP for your site
- Your hosting server returns your website’s files
So in summary:
- DNS translates the domain name into your hosting provider’s IP address
- Your web host receives the request and delivers your site at that IP
It’s the combination of pointing your domain’s DNS to your host’s IP, and hosting your site’s content on their servers that enables visitors to access your site online.
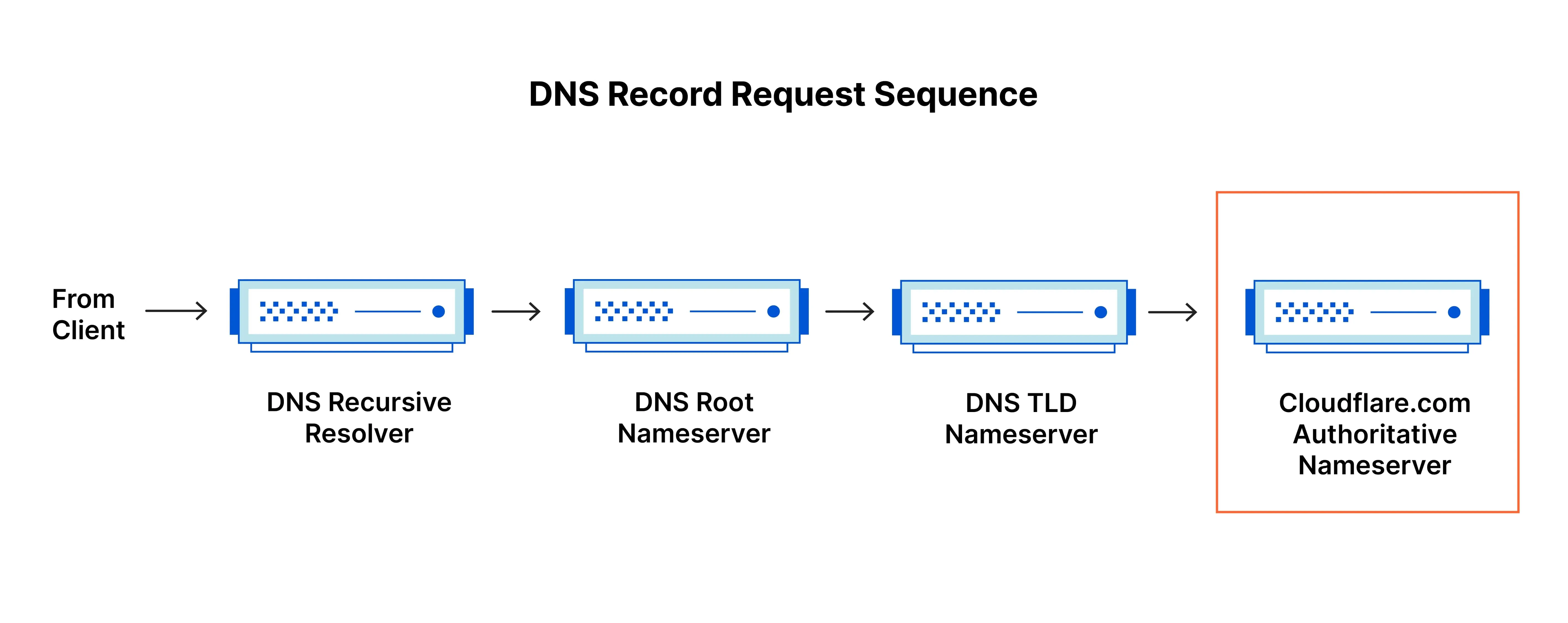
Key Differences Summarized
DNS
Web Hosting
Purpose
Translates domains into IPs
Provides servers to host sites
What it does
Points domains to hosting IPs
Stores and delivers site files
Necessity
Required for human-friendly domain names
Required to put your site on the internet
Set up process
Register and configure domains
Sign up for hosting plan
So in summary:
- DNS handles the domain mappings
- Hosting delivers your actual site content
- Both are needed for a website to be accessible online!
I hope this overview helps explain the core differences between DNS and web hosting and how they work hand-in-hand to publish your site. Let me know if you have any other questions!
Read Count: 0
 Facebook
Facebook
 Twitter
Twitter
 Email
Email